The most important resin binders in modern paint are acrylic polymers, alkyd polymers, and epoxy polymers. The chemical production process of each is described below.
Acrylic Polymers
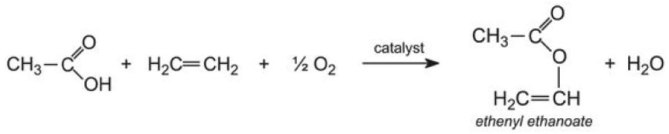
These resins are used in most common household paints. They are composed of polymers or co-polymers of ethenyl ethanoate and a propenoate ester. Ethenyl ethanoate is produced by passing a combination of ethanoic acid vapor, ethane, and oxygen over heated palladium and copper chlorides. This chemical process is shown below.
The chemical process above creates Ethenyl ethanoate and an acrylic ester which copolymerize at random. These are shown below.
Alkyd Polymers
These are used for decorative glossy paints. It is produced from a polyol, which is a triol combined with a dibasic acid and a drying oil. When the mixture is heated, ester links are formed with water as the byproduct. The chemical process is shown below.
The above process forms a monoglyceride which reacts with the anhydride which forms the alkyd polymer, shown below.
Epoxy Polymers
These are used as industrial primers to provide resistance to chemical corrosion. They are produced from 3-chloropropene combined with substituted phenols. This chemical process is shown below.